Which Is the Best Description of a Normal Fault
The san andreas fault is. Hanging wall and footwall have moved.

Fault Types What Are The Three Main Types Of Faults Geology Page
Relative stratigraphic offset of normal fault a function of.
. Right-lateral - This is a type of strike-slip. Fault Fracture in two mats with relative movement. Inclined dip-slip faults in which hanging wall has moved down relative to footwall 1 younger rocks placed on older rocks by fault 2 Crustal extension driving process 2.
Strike-slip Now you can substitute these terms. Normal faults occur where two blocks of rock are pulled apart as by tension. Hanging wall and footwall have moved horizontally in a right-lateral sense.
Strike-slip general - Fault motion is parallel to the strike. Faults form when one section of the land moves downward because tectonic forces are pulling the land apart. Footwall has moved down relative to the hanging wall.
Normal Fault The upper block moves downward relative to the lower block. Where the fault plane is sloping as with normal and reverse faults the upper side is the hanging wall and the lower side is the footwall. Reverse - Hanging wall moves up relative to footwall.
Which is the best description of a normal fault. What the theory that the sun goes around earth was replaced with the theory that earth goes around the sun this was an exaple of a. These cracks are faults.
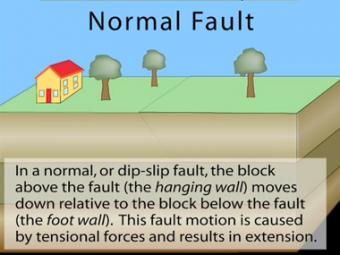
The term footwall is derived from miners finding mineral deposits where inactive faults have been filled in with mineral deposits at their feet. A geologic fault in which the hanging wall has moved downward relative to the footwall. Detailed Description Normal or Dip-slip faults are inclined fractures where the blocks have mostly shifted vertically.
In geology a fault refers to a planar fracture or. If the rock mass above an inclined fault moves down the fault is termed normal whereas if the rock above the fault moves up. This type of faulting occurs in response to extension and is often observed in the Western United States Basin and Range Province and.
Left-lateral - This is a type of strike-slip. Normal fault - a dip-slip fault in which the block above the fault has moved downward relative to the block below. See more at fault.
A normal fault will have a hanging wall and a footwall. Dip-slip 3 Strike-slip fault Both blocks slide horizontally across one another. Normal Fault is when a tectonic plate appears to have moved down the fault and the fault is said to be a normal fault.
Best description of a normal fault. A geologic fault in which the hanging wall has moved downward relative to the footwall. The best description of the relative movement across the normal fault depicted in Figure 38 is that the a.
1 Show answers Another question on Biology. 4 min read. The main difference between normal fault and reverse fault is that normal fault describes the downward movement of one side of the fault with respect to the other side whereas reverse fault refers to the upward movement of one side of the fault with respect to the other side.
The American Heritage Student Science Dictionary Second Edition. The earthquake focus is the place where the rocks break along the fault plane. It is a flat surface that may be vertical or sloping.
Noun an inclined fault in which the hanging wall has slipped down relative to the footwall. Normal - Hanging wall moves down relative to footwall. A geologic fault in which the hanging wall has moved downward relative to the footwall.
Normal faults occur where two blocks of rock are pulled apart as by tension. Hanging wall has moved down relative to the footwall. The opposite of this in which one side.
Normal Fault A fault in which the hanging wall has moved downward relative to the footwall usually happens where tension exists in the crust or it is being pulled apart. Best description of a normal fault. See Note and illustration at fault.
Opposite side displaced to the left. The line it makes on the Earths surface is the fault trace. Normal faults occur where two blocks of rock are pulled apart as by tension.
A fault which is a rupture in the earths crust is described as a normal fault when one side of the fault moves downward with respect to the other side. A fault that forms at a divergent boundary. One rock face slips down past the other rock face due to.
The earthquake epicenter is the point directly above the earthquake focus on the Earths surface. Hanging wall is where the ore is eroding out of the rocks. Separation and Normal Faulting a.
A normal fault also called tension fault and gravity fault is formed when there is tension and the rock is being pulled apart from itself. Dip-slip 2 Reversethrust Fault The upper block moves upward relative to the lower block. When the fault plane is vertical there is no hanging wall or footwall.
Opposite side displaced to the right.

Normal Fault U S Geological Survey

Fault Types 3 Basic Responses To Stress Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology
12 3 Fracturing And Faulting Physical Geology

Types Of Faults Slipe Strike Normal Reverse Earth And Space Science Science Videos Geology
No comments for "Which Is the Best Description of a Normal Fault"
Post a Comment